Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saiki, Seiichi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Hiroki, Akihiro; Morishita, Norio; Tamada, Masao; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Shinichi; Maeyama, Takuya*; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Baldacchino, G.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Murakami, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
Recently, cancer therapy with high-energy heavy ions has been utilized, showing high efficiency in actual treatment. While its effectiveness has already been certificated phenomenologically, detailed mechanism through which such a feature appears has not been clarified yet. Water is a main component of human body, and then, it is inevitably important to comprehend water radiolysis. In this study, water radiolysis near the Bragg peak was focused on because the peak is overlapped to cancer in actual treatment, and yield of hydroxyl radical ( OH) has been determined because
OH) has been determined because  OH is assumed as a species most responsible to indirect action. In addition, contribution of fragmentation reactions which is significant for high-energy heavy ions were discussed from the viewpoint of
OH is assumed as a species most responsible to indirect action. In addition, contribution of fragmentation reactions which is significant for high-energy heavy ions were discussed from the viewpoint of  OH yield.
OH yield.
Maeyama, Takuya*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Baldacchino, G.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Sihver, L.*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
Yield of hydroxyl radical ( OH) has been measured near the Bragg peak of therapeutic heavy ions. Such a highly energetic heavy ions go through fragmentation reactions and its contribution has been quantitatively estimated with computer simulation. There are two kinds of simulation codes. One it deterministic 1D code, which needs only a few minutes for single calculation, and the other is stochastic 3D code, which can be extended to wide variety of beam configurations and more close to real situation. However, comparison of them has not been attempted intensively. In this study, measured
OH) has been measured near the Bragg peak of therapeutic heavy ions. Such a highly energetic heavy ions go through fragmentation reactions and its contribution has been quantitatively estimated with computer simulation. There are two kinds of simulation codes. One it deterministic 1D code, which needs only a few minutes for single calculation, and the other is stochastic 3D code, which can be extended to wide variety of beam configurations and more close to real situation. However, comparison of them has not been attempted intensively. In this study, measured  OH yield has been reproduced by considering fragmentations based on these code and results were compared to extract advantages and disadvantages of them.
OH yield has been reproduced by considering fragmentations based on these code and results were compared to extract advantages and disadvantages of them.
Maeyama, Takuya*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Baldacchino, G.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
Yield of hydroxyl radical ( OH), which is assumed to be most responsible species in indirect action, has been measured near the Bragg peak of therapeutic heavy ions. Such a highly energetic heavy ions go through fragmentation reactions, leading to production of lighter ions. Contribution of fragmentation to dose and so on increases near the Bragg peak. In this study, fragmentation reactions are simulated with PHITS code, which is developped by a group of JAEA. In the trial, the same irradiation system as used in actual experiment was taken into account, and each fragmentation ion was estimated quantitatively. In addition, measured
OH), which is assumed to be most responsible species in indirect action, has been measured near the Bragg peak of therapeutic heavy ions. Such a highly energetic heavy ions go through fragmentation reactions, leading to production of lighter ions. Contribution of fragmentation to dose and so on increases near the Bragg peak. In this study, fragmentation reactions are simulated with PHITS code, which is developped by a group of JAEA. In the trial, the same irradiation system as used in actual experiment was taken into account, and each fragmentation ion was estimated quantitatively. In addition, measured  OH yield was reproduced by using established knowledge.
OH yield was reproduced by using established knowledge.
Izumi, Yudai*; Imazu, Akiko*; Mimoto, Aki*; Tanabe, Maiko*; Nakagawa, Kazumichi*; Tanaka, Masahito*; Agui, Akane; Muro, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirade, Tetsuya; Lee, J.
no journal, ,
Quantum beats were detected in the reaction of electron-spin-correlated pairs of ortho-positronium and hydroxyl radical. Singlet ortho-positronium and hydroxyl radical pairs were generated in positron radiolysis of water molecules. The singlet-triplet transition caused via the hyperfine coupling of every radical affects the rate of the radical reaction, and then affects the rate of the competing reaction, the spin conversion reaction between ortho-positronium and hydroxyl radical. Spin conversion of ortho-positronium can possibly be detected using positron annihilation age-momentum correlation (AMOC) measurements, and time resolved annihilation  -ray energy distribution observed using AMOC measurements did successfully reveal quantum beats in water.
-ray energy distribution observed using AMOC measurements did successfully reveal quantum beats in water.
Asano, Masaharu; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nunung, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Maekawa, Yasunari
no journal, ,
PVDF thin films irradiated with four kinds of ion beams were etched in a 9 M KOH aqueous solution after their exposure to different oxidizing environments. The irradiation of higher-LET ions, causing each track to more concentrated damage, was preferable to achieve high sensitivity of the etching. Very interestingly, an ozone treatment was found to enhance largely an etch rate in the latent track without a significant change in a bulk etch rate, thereby enabling us to obtain very high etching sensitivity for the preparation of nano-sized through-pores.
Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Sugo, Yumi; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kimura, Atsushi; Hirota, Koichi; Katsumura, Yosuke*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 in the oxidation of VOC in air using an electron beam irradiation/catalytic process
in the oxidation of VOC in air using an electron beam irradiation/catalytic processHakoda, Teruyuki; Mizuno, Akira*; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oka, Toshitaka; Yamashita, Shinichi; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Saiki, Seiichi; Muroya, Yusa*; Lin, M.; Kamibayashi, Masato*; Anzai, Kazunori*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
Detection and quantification of the oxidative radicals such as hydroxyl radical or superoxide anion radical are very important to clarify the biological oxidative damages. These oxidative radicals, produced by water decomposition with  -ray irradiation, were detected as spin adducts of CYPMPO and themselves. In this work, reactivity CYPMPO and behavior of spin adducts were investigated.
-ray irradiation, were detected as spin adducts of CYPMPO and themselves. In this work, reactivity CYPMPO and behavior of spin adducts were investigated.
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Aoyagi, Noboru; Shinha, Yusuke; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
no journal, ,
Radiolytic behavior of ionic liquids of thiocyanate salts was studied by using the ns-pulse radiolysis technique. The transient absorption of thiocyante dimer radical ion was observed in the liquids, and the rise was within the width of electron pulse. The maximum absorbance of dimer in the liquids was equivalent to that in aqueous solutions, where the dimer is formed from the reaction of thiocyanate ion with OH, and increased linearly with increasing the thiocyanate concentration in the liquids. These indicate that one of the ionization sites of liquids should be thiocyanate ion.
Muroya, Yusa*; Lin, M.; Han, Z.*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Ueda, Toru*; Mostafavi, M.*; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
A new ultrafast pulse radiolysis system was developed which enables to perform the experiments at high temperature/pressure condition covering supercritical condition. Fast spur decay kinetics as well as optical spectra of a hydrated electron in picosecond time scale at elevated temperature up to supercritical condition were observed for the first time.
Muroya, Yusa*; Lin, M.; Han, Z.*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Ueda, Toru*; Mostafavi, M.*; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
By employing a newly developed high temperature - ultrafast pulse radiolysis system, temperature dependence of spur decay kinetics of the hydrated electron from room temperature up to supercritical condition was successfully measured. Faster spur decay within a few nanosecond was observed as increasing temperature. Picosecond yield of the hydrated electron at supercritical condition was also evaluated. The initial yield was found to show strongly density dependence of water.
Kumagai, Yuta; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yamada, Reiji; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
no journal, ,
Reactions of radical products of water radiolysis in the presence of colloidal silica were studied by time-resolved optical absorption measurement using pulse-radiolysis technique. Consequently scavenging reaction of colloidal silica toward OH radical was observed. Then scavenging capacities of colloidal silica samples of different sizes were measured. The results showed that colloidal silica of smaller size has larger scavenging capacity for unit amount added to solutions.
Kumagai, Yuta; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yamada, Reiji; Katsumura, Yosuke*
no journal, ,
Reactions of OH radical in the presence of silica gel were studied in perchloric acid solution of dichromate ion by addition of 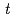 -butanol or silver ion as a scavenger of OH radical. The reduction yield of dichromate ion was increased in the presence of silica gel but the effect was suppressed by addition of OH radical scavengers. These results indicate that there is an interaction between silica gel and OH radical, which, leads to increase in the reduction yield of dichromate ion.
-butanol or silver ion as a scavenger of OH radical. The reduction yield of dichromate ion was increased in the presence of silica gel but the effect was suppressed by addition of OH radical scavengers. These results indicate that there is an interaction between silica gel and OH radical, which, leads to increase in the reduction yield of dichromate ion.
Chen, J.; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari
no journal, ,
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) films were modified by thermal grafting of divinylbenzene (DVB) followed by radiation grafting of ethyl styrenesulfonate (ETSS), to develop a polymer electrolyte membrane for use in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells or direct methanol fuel cells. The DVB-grafting considerably enhanced the subsequent ETSS-grafting. The ETSS units were converted to styrenesulfonic acid units by hydrolysis in water, resulting in a PEEK/DVB polymer electrolyte membrane. This new membrane was tested in a fuel cell, and a high cell performance was confirmed. Therefore, we conclude that this modified PEEK film can be used as the PEM for the application in fuel cells.
Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Yamashita, Shinichi; Muroya, Yusa*; Lin, M.; Kamibayashi, Masato*; Anzai, Kazunori*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
5-(2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propoxy cyclophosphoryl)-5-methyl-1pyrroline N-oxide (CYPMPO) is a recently developed spin-trapping agent, which is expected to distinguish O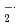 from
from 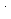 OH. We have determined its reactivity with water decomposed radicals, especially with
OH. We have determined its reactivity with water decomposed radicals, especially with  OH and with e
OH and with e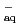 by pulse radiolysis, and compared results with commonly-used spin trapping agent, 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO). Furthermore, the reactions with oxidative radicals such as
by pulse radiolysis, and compared results with commonly-used spin trapping agent, 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO). Furthermore, the reactions with oxidative radicals such as  COO
COO , NO
, NO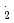 and Br
and Br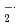 have also been investigated.
have also been investigated.
Yamada, Reiji; Kumagai, Yuta; Nagaishi, Ryuji
no journal, ,
Hydrogen production due to irradiation of Co-60  -ray was studied under different dose rates of
-ray was studied under different dose rates of  -ray as well as different species of oxides and metals added to aqueous solutions. Concerning the dose rate dependence the hydrogen production yield was scarcely influenced with the rate in the case of solutions without oxides but it was done in the case of solutions with oxides. When aqueous solutions were added with metals in stead of oxides, there was no enhancement of hydrogen production, which was observed in the mixtures of water and oxides.
-ray as well as different species of oxides and metals added to aqueous solutions. Concerning the dose rate dependence the hydrogen production yield was scarcely influenced with the rate in the case of solutions without oxides but it was done in the case of solutions with oxides. When aqueous solutions were added with metals in stead of oxides, there was no enhancement of hydrogen production, which was observed in the mixtures of water and oxides.
Kumada, Takayuki; Noda, Yohei; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji
no journal, ,
We succeeded in dynamically polarizing UV-irradiated solid butanol. Unlike persistent radicals such as TEMPO, the butyl radicals produced by the UV-photolysis immediately decay by melting. We propose that free radicals produced by UV-photolysis are applicable to DNP-enhanced hyperpolarized liquid-state NMR.
Hata, Kuniki; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Fu, H. Y.*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Nakagawa, Keiichi*; Nakagawa, Hidehiko*
no journal, ,
In order to investigate the reaction mechanism of edaravone (3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin- 5-one) with OH, the reactivity of edaravone derivatives which have different substituent from edaravone was observed by pulse radiolysis system. From the experiments, OH-adduct radical formed by the addition of OH to phenyl group has been identified as a main intermediate.